blog post
Generative AI: A Game-Changer in Cybersecurity
In the few months following its public emergence, generative AI has shown immense potential to revolutionize cybersecurity operations and products. The debut of ChatGPT and other tools powered by large language models (LLMs) marks a significant turn in the cybersecurity industry, with generative AI poised to become a fundamental tool. However, challenges persist, particularly in sourcing high-quality, comprehensive datasets for training LLMs, due to the sensitive and compartmentalized nature of security data.
A Predominant Transformative Impact is in Threat Identification (In the Detection and Analyst phase of the NIST Incident Response Lifecycle)
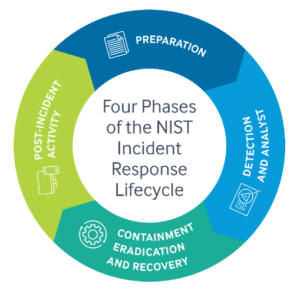
Our analysis reveals that in the cybersecurity sector, the application of generative AI is predominantly in the threat identification phase of the incident response framework. This technology is enhancing the speed and accuracy with which analysts can identify and assess the scale of cyber-attacks. Its capability to filter out false positives and to detect and hunt threats is becoming increasingly dynamic and automated.
Varied Adoption across Incident Response Stages
While adoption in the containment, eradication, and recovery phases is less uniform, generative AI is making strides. It aids in bridging knowledge gaps by providing analysts with actionable recovery instructions based on past incidents. However, the path to full automation in these stages remains long, with significant human oversight still necessary.
Lessons Learned and Report Generation
Generative AI is also finding its way into the lessons-learned stage. Tools like Google’s Security AI Workbench are automating the creation of incident response reports, which, when fed back into the system, enhance future defenses. However, the need for human involvement in this process is expected to persist.
A Double-Edged Sword
The flip side is the potential misuse of generative AI by cybercriminals. There are increasing instances of malicious actors employing tools like ChatGPT for sophisticated phishing attacks and malware creation. The dark web has seen a proliferation of discussions around generative AI, with hackers boasting about leveraging these tools for malicious purposes.
Recommendations for Corporate and Cybersecurity Leaders
Given this landscape, it’s crucial for corporate leaders and CISOs to:
- Recognize that generative AI doesn’t simplify cybersecurity’s operational and technical challenges.
- Prioritize discussions on generative AI and cybersecurity in high-level meetings, advocating a holistic approach.
- Validate generative AI outputs in threat detection and train personnel to balance reliance on AI with traditional threat hunting skills.
- Diversify reliance on vendors and AI models to mitigate risks.
Cybersecurity Firms: A Balancing Act
Cybersecurity companies should strike a balance by integrating generative AI capabilities while guarding against the creation of AI-induced false information and vulnerabilities. Hiring talent adept in both cybersecurity and AI is key to navigating this evolving landscape.
Staying Ahead of the Curve
As generative AI continues to advance, staying updated and strategically adaptive is essential for all stakeholders, from cybersecurity providers to enterprises. This will ensure they leverage the benefits of generative AI while maintaining robust defenses against an increasingly sophisticated threat environment.
Author
Steve King
Managing Director, CyberEd
King, an experienced cybersecurity professional, has served in senior leadership roles in technology development for the past 20 years. He has founded nine startups, including Endymion Systems and seeCommerce. He has held leadership roles in marketing and product development, operating as CEO, CTO and CISO for several startups, including Netswitch Technology Management. He also served as CIO for Memorex and was the co-founder of the Cambridge Systems Group.

